Robotic Process Automation
RPA – Robotic Process Automation
Robotics Process Automation (RPA) is at the forefront of human-computer technology and
provides players in the industry with a virtual workforce that is ruled based and is set
up to connect with your company’s systems in the same way as your existing users.
With robotics, you automate and build an automation platform for you front office, back
office and support functions.
5 Factors in Choosing Which Processes to Automate
Employee Involvement
“99% of organizations still spend considerable personnel time doing repetitive manual
tasks, with almost three quarters (74%) spending over a quarter of their time doing so.”
Complexity
Complexity of a process can be defined by the number of applications/systems, the
frequency of human intervention, or the number of steps required in order to execute the
task.
Volume
Organizations do not have a defined set of opening hours, meaning a high volume of
orders, requests, and complaints are received around the clock, regardless of weekends
and holidays.
Standardization and Stability
RPA is best most suited for automating tasks that are highly definable and occur the same
way every time. These activities are be rules-based, consistent and data driven.
Difficulty
of Outsourcing Many business activities, especially in financial services, require a high
level of regulatory compliance. This kind of security is often difficult to achieve and
maintain with offshoring because companies have a lesser degree of oversight and direct
control when processes are managed by a BPO provider.
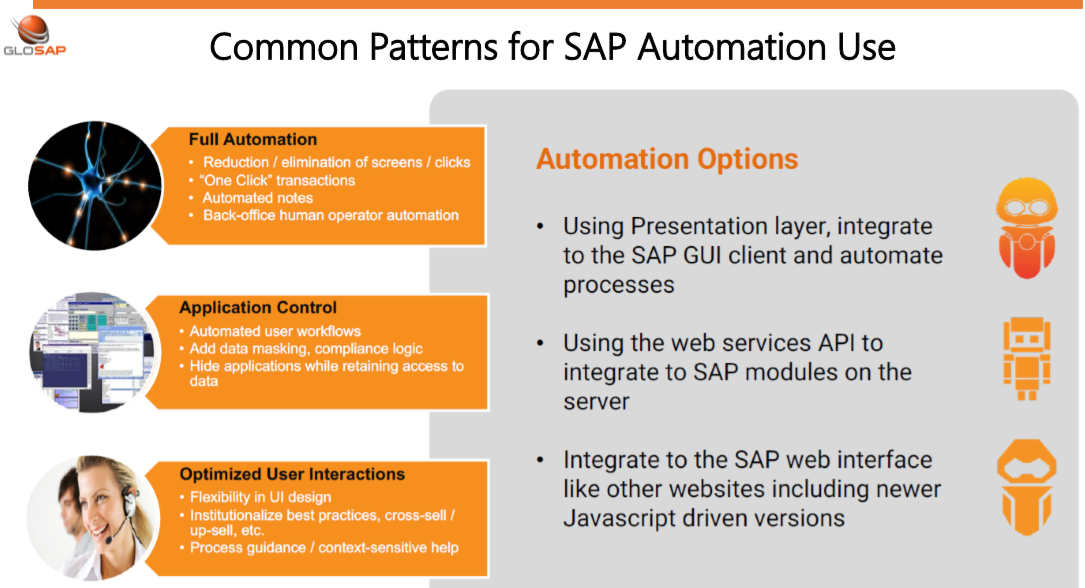
How does it work?
RPA is machine and software automation that frees humans by mimicking human activity in manual, tedious, repetitive, rules-based transactions, processes and workflows, initiating responses and communicating with digital systems.
✓ Multi-system access (SAP, Oracle, AX, CRM, Excel / Access, legacy systems, other 3rd Party systems..)
✓ Clearly defined rules-based processes, Limited exceptions and human intervention
✓ Structured sets of data Documentation and standardized transactions.
✓ Deep SAP integration, low-cost implementation and Quick Deployment [ Around 3 to 4 Weeks]
✓ Simple, Frequent, repetitive, fast automation for business users to any areas of SAP
✓ No Manual data input from human and no errors. [ Fully Automated front office / Back office Robo]
✓ Reduce operational costs, increase efficiency, improve productivity and accelerate performance.
| Oracle | AX| SAP Sales & Distribution (SD) | SAP MM | Supply Chain (SCM) | SAP HCM | SAP FICO |
RPA reduces manual processes, saves time and money
RPA is an emerging automation technology that manages, executes and monitors any
repetitive front-office and back-office processes that do not require human judgment,
allowing employees to focus on the more sophisticated tasks.
In other words, RPA software allows developers to tailor complex automations to a
company’s processes. When an RPA robot is at work, it performs tasks just like a human
activity like logging in, operating applications, entering data, performing complex
calculations and logging out.
This is a cutting-edge digital solution that will capturing and interpreting existing
applications for processing a transaction, include data entry, data verification, copying
and pasting of data, data conversions, selection, interfacing between several
applications, reports generation, triggering responses and communicating with other
digital systems.
Glosap will provide you with perfect Robotic Process Automation (RPA) that aims at
automating and integrating data with manual activities. RPA is used across diverse
industries such as Manufacturing, Trading, insurance, banking, Finance and logistics.
SAP RPA – Front office Robo
The customer is an essential part to the success of every business. While back office
automation is important in order to alleviate strain and provide support to the front
office, front office automation can completely transform how companies interact,
communicate, and engage with their customers.
RPA in the front office can: "assist your agent, making them more productive and
improving your customer experience with shorter transaction times, reducing manual errors
and avoiding the highly irritating repeat questions for the same information.
It can also open up new channels of communication on your existing systems
such as responding to customer’s balance enquiries by text.”
SAP RPA – Front office Robo
It’s true that a lot of business processes perfect for RPA are traditional back office
tasks – HR, Logistics, SCM, Finance & accounting, moving data between
databases, etc. In today’s business environment, leading enterprises need up-todate, innovative ways to
optimize workflows in the back office. Moving data between multiple applications and
systems, handling complex data entry, and keeping records updated are processes that
cost a lot of time and money and are inevitably prone to human error. By automating
these repetitive tasks and eliminating redundancies, robotic process automation enables
you to operational efficiency and speed and delivers fast ROI.
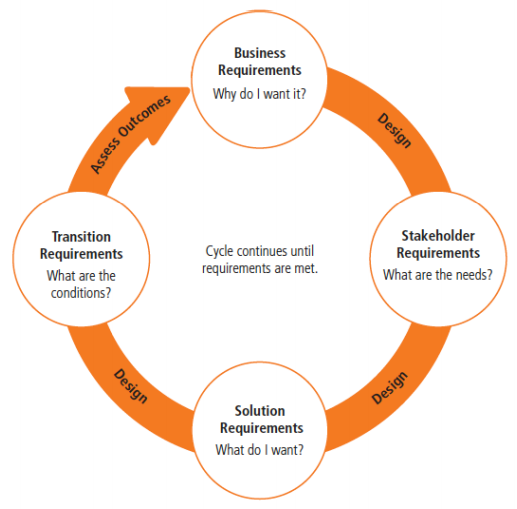
Critical First Step - Process Discovery
A good business requirements document (BRD) and Process Definition Document (PDD) helps
to execute automation projects “run like factory” with predictable outcomes and on time…
1. Process Selection for Automation
- Business impact
- Benefit
- Timing
2. Transaction Selection by Robot
- By Type
- By Value
- FIFO, LIFO, Random
3. Existing Process Maturity
RPA for Finance Automation ( SAP \ Oracle \ AX \ FINANCE )
Finance - Pre-calculated credit to a customer’s account
The Standard process performed by a Financial Person is as follows:
✓ The Financial Person runs a report in ERP to extract the payment record of a
specific customer for the last 3 / 6 months.
✓ The data from the report is copied into a spreadsheet to analyse the risk, and
calculate a revised credit rating.
✓ The credit limit is then applied to the customer’s account in the ERP System.
✓ The system will do the credit check & block the order after that.
Three Biggest Challenge of Finance Automation [RPA]
Treating RPA as a Legacy IT Deployment Is Causing Challenges for Finance Teams
“Unlike many new technologies, RPA has the potential to deliver significant business
benefits on day one,” To deploy RPA successfully finance leaders must embrace a new
mindset. Unless finance departments take a more agile approach when implementing RPA,
they are likely to experience failures at each phase of implementation and won’t realize
the full potential of the technology.
"RPA promises to speed up and automate routine processes while reducing the amount of errors, which in turn will enable human team members to pursue higher value tasks that cannot be easily automated"
1. The Planning Stage:
RPA deployments often fail to deliver on expectations because they are planned as
an end-to-end process, rather than focused on a single activity within a
process. A focus on mapping an entire process before
automating a single activity will delay implementation significantly and,
in fact, create extra work. This is because, once one activity
has been successfully automated, the code can be quickly applied to other similar
activities within the same or different processes.
“Finance departments can start relatively conservatively with RPA by focusing on using
one bot against a number of individual activities. It’s still conservatively possible
to see an output gain of up to 10 times, compared
with a full-time employee working during the same amount
of time.”
In this way, organizations can reap immediate efficiency gains from RPA, without investing a lot
of time planning, standardizing and implementing. Then, when gains have been
realized and the pilot is working well, they can move to other similar activities
and processes in an agile, iterative way..”
Recommends that finance leaders focus on identifying the areas of responsibility needed
to manage RPA, rather than relying on traditional, fixed roles for this
purpose. Finance department leaders should account for the new competencies needed for
successful RPA management, centered around digital process design. These are largely
hard-to-train competencies and organizations will likely need new hiring processes to
ensure the right skills for the job.
2. The Building Stage:
In this stage, difficulties again occur when leaders treat RPA deployment the same way
as they have legacy technology projects.
Traditional technology deployments have relied on a “
big bang” approach, where the majority of potential use cases are mapped and
tested before the project is implemented. A list of requirements is generated and vendors
are asked to submit their proposals.
“You don’t need to figure out every possible use case and requirement of an RPA solution
before you begin,” This will just result in spending more time and money than is really
needed.
3. The Testing Stage:
Relying too much on IT teams and vendors to identify the issues and needs for deploying
robots often causes failures in the testing stage. The organization’s RPA team should
take the lead in clarifying and directing support needed from IT and vendors at the
appropriate times.
clearly defining responsibilities for RPA activities so that the RPA and IT teams deal
efficiently with issues such as setting up and monitoring robot performance, with IT
providing support for the underlying technology infrastructure. Due to the highly
iterative nature of RPA technology, and the unique needs of the business it addresses,
the most important aspects of managing robotics requires internal steering.
“The benefits of successful RPA deployments within finance include a reduction in errors
from manual work and a redeployment of full-time employees to higher value activities,”
“But robots are only as good as the people who design and manage them. CFOs should start
any RPA deployment by ensuring they understand the new agile mindset needed to implement
the technology, with the right competencies in place to manage it.”
Let's deliver the right solution for your business!